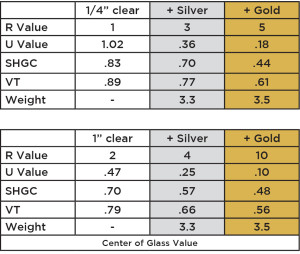
This table below uses software developed by the Department of Energy which allows anyone to simulate the thermal performance of windows using different spacing and materials. By using this, we can easily show the difference in the most common glass existing in commercial buildings and how the performance in amplified by placing a RetroWAL™ system behind it.
The first column is the existing window (1/4 or 1” IGU) with performance values on the left hand side. A glossary is shown below but to summarize, the insulating value of the combined window system is increased 3 times with RetroWAL™ Silver and 5 times RetroWAL™ Gold. For existing 1-inch insulated glass units without a low-e coating or inert gas, the thermal performance is increased 2 and 5 times with RetroWAL™.
The two examples above use Windows 6.3 modeling software. In each case, the RetwoWAL™ system utilizes a 2” airspace from the existing window. The IGU is uncoated and has a ½ airspace. These values are for COG or Center of Glass.
One other factor not taken into consideration in this table is the reduction in air leakage around the gaskets of the glass. RetroWAL™ has been tested to reduce the airleakage down to .01 cfm/ft2.
R Value: This is the measure of thermal resistance and is in the English units BTU/(h °F ft2).
U Value: This is the reciprocal of R value and is used in the fenestration and window industry.
SHGC: This is the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient and is the energy transmittance of the glass window due to solar radiation. It ranges from 0 or totally blocked to 1 or direct sunlight.
VL: Is the Visible Light transmitted through the glass. The idea is to maximize the amount of natural light but to minimize the solar heat of infrared radiation. The values range from 0 to 1.
Weight: This is the additional weight per square foot the RetroWAL™ system adds to the window opening. In large curtain wall buildings it is important to maintain the structural integrity of the window and add as little weight as possible.